Sea level rise and adaptation under the California Coastal Act
Explore how the California Coastal Act helps mitigate sea level rise, protect coastal communities, and restore natural defenses.

As climate change continues to impact California’s coastlines, the California Coastal Act plays a key role in mitigating the effects of sea level rise and preparing coastal communities for long-term adaptation. This page outlines the steps taken to address rising sea levels, protect communities, and preserve the natural resilience of California’s coastal environment.

Understanding Sea Level Rise in California
The effects of sea level rise are already being felt along California’s coastline. Increased flooding, erosion, and higher tides are threatening both natural ecosystems and coastal infrastructure. The Coastal Act addresses these challenges by guiding development, enforcing protective measures, and ensuring that adaptation strategies are in place.
- Increased Flooding: Coastal cities and low-lying areas are experiencing more frequent flooding due to rising sea levels and higher storm surges.
- Erosion of Coastal Bluffs and Beaches: As sea levels rise, the natural protective barriers of cliffs, dunes, and beaches are eroded, leading to the loss of land and habitat.
- Infrastructure at Risk: Public infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and utilities, are increasingly at risk from erosion and flooding, especially in areas where development has occurred too close to the waterline.

Climate Adaptation Measures in the Coastal Act
The California Coastal Act includes provisions to adapt to and mitigate the impacts of sea level rise. These measures ensure that new developments, as well as existing structures, are resilient to the changing climate.
- Development Guidelines: New coastal developments are required to consider sea level rise in their planning stages. This includes the construction of buildings that are set back from vulnerable areas or elevated to avoid flood risk.
- Erosion Control: Projects that involve controlling erosion, such as the construction of seawalls or bluff stabilization, must be designed to protect both the development and the natural shoreline. These projects are closely regulated to ensure they do not exacerbate erosion in other areas.
- Wetland Restoration: Wetlands play a crucial role in buffering coastal areas from flooding. The Coastal Act encourages the restoration and expansion of wetlands, which can absorb floodwaters and protect inland areas.
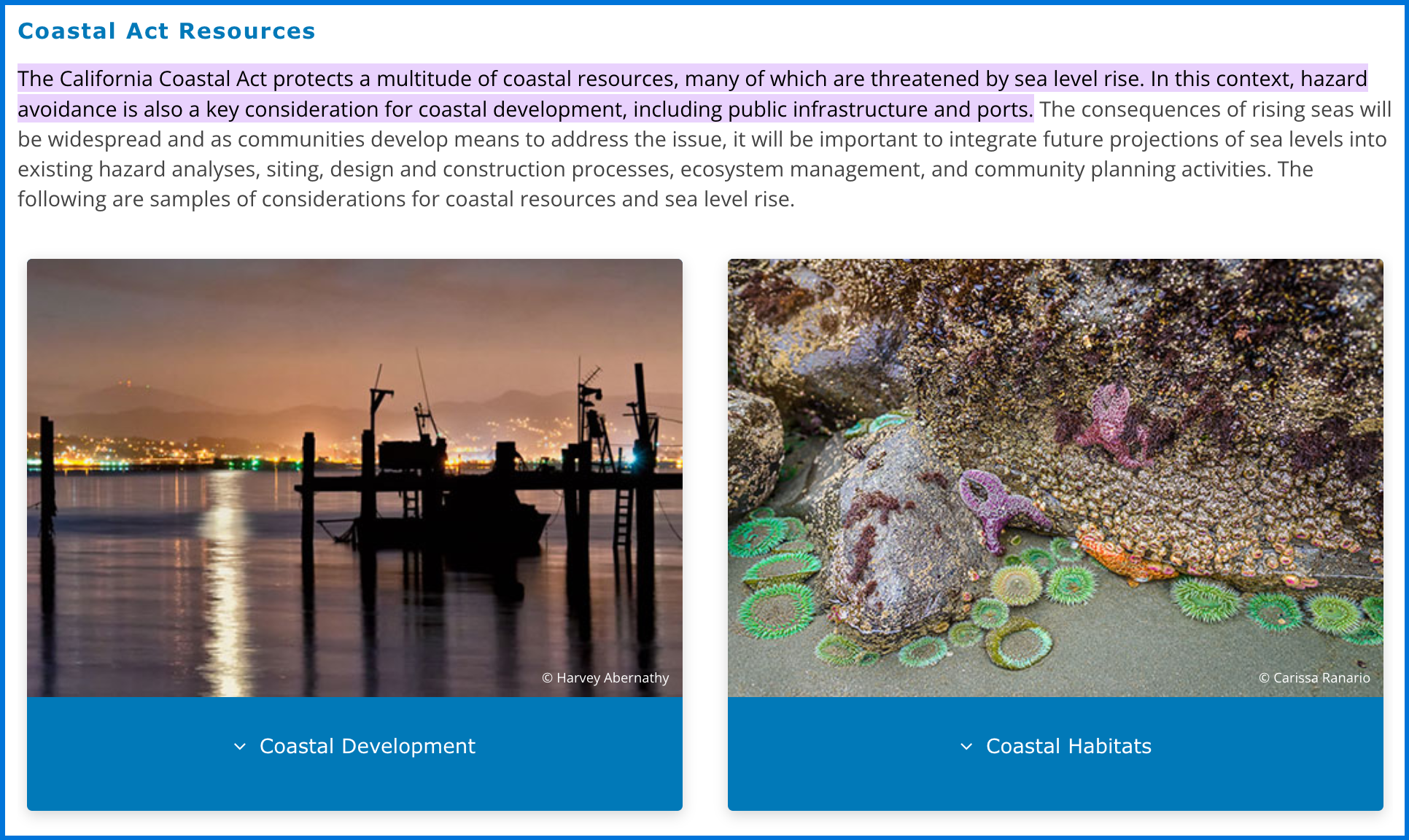
Protecting Coastal Communities
The Coastal Act not only protects natural ecosystems but also focuses on safeguarding the communities that live and work along California’s coast. Key strategies include:
- Planning for Resilient Infrastructure: Coastal infrastructure, including roads and public utilities, must be adapted or relocated to reduce vulnerability to flooding and erosion. The Coastal Commission works with local governments to plan and implement these changes.
- Community Education: The Act promotes public awareness campaigns to educate coastal residents about the risks associated with sea level rise and how they can prepare their homes and businesses.
- Relocation and Managed Retreat: In some high-risk areas, the Coastal Commission may recommend the relocation of communities and infrastructure through a process known as managed retreat. This approach allows vulnerable areas to return to a natural state, reducing long-term risk.

Preserving Natural Coastal Defenses
Natural features like dunes, wetlands, and bluffs offer vital protection against the impacts of rising sea levels. The Coastal Act prioritizes the preservation and restoration of these natural defenses to maintain the resilience of California’s coastline.
- Dune Restoration: Dunes provide a natural buffer against waves and storm surges. Projects to restore or rebuild coastal dunes are encouraged under the Act, helping to protect both ecosystems and communities.
- Wetland Expansion: Wetlands act as sponges, absorbing floodwaters and reducing the impact on inland areas. The Coastal Act supports the expansion of wetlands to provide natural flood protection.
- Bluff Stabilization: Coastal bluffs are vulnerable to erosion, which can endanger homes and infrastructure. Stabilizing bluffs using environmentally sensitive methods is a key part of managing the effects of sea level rise.
Conclusion
The California Coastal Act plays a critical role in addressing the challenges posed by sea level rise. Through a combination of development restrictions, restoration projects, and community engagement, the Act ensures that California’s coastline remains resilient in the face of climate change. As the climate continues to change, the Coastal Act will be essential in protecting both the natural and built environments along the coast.